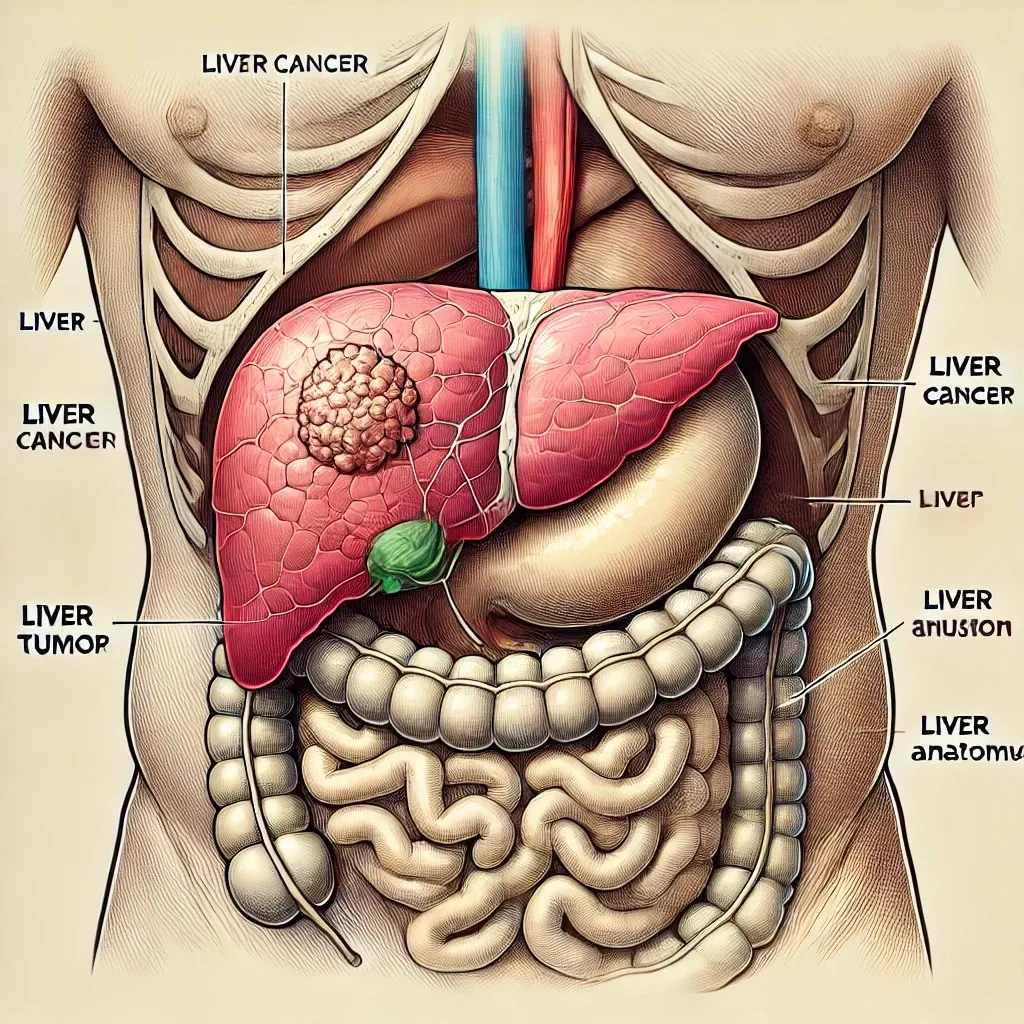
Liver cancer, also known as hepatic cancer, originates in the liver, a vital organ located in the upper right abdomen. The liver plays a crucial role in filtering toxins from the blood, producing bile for digestion, and storing energy. Liver cancer can be aggressive and requires prompt medical attention.
Types of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer is classified into primary and secondary types:
- Primary Liver Cancer: Begins in the liver itself. The main types include:
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): The most common type, originating in the main liver cells called hepatocytes.
- Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer): Starts in the bile ducts within the liver.
- Angiosarcoma and Hemangiosarcoma: Rare cancers that originate in the blood vessels of the liver.
- Secondary (Metastatic) Liver Cancer: Cancer that has spread to the liver from other parts of the body, such as the colon, breast, or lung.
Symptoms
Symptoms of liver cancer can vary but often include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Upper abdominal pain or discomfort
- Nausea and vomiting
- General weakness and fatigue
- Swelling or fluid buildup in the abdomen (ascites)
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- White, chalky stools
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing liver cancer:
- Chronic hepatitis B or C infection
- Cirrhosis (scarring of the liver) from alcohol abuse or other liver diseases
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Exposure to aflatoxins (toxins produced by certain fungi in food)
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Family history of liver cancer
- Long-term use of anabolic steroids
Diagnosis
Diagnosing liver cancer involves several steps:
- Medical History and Physical Exam: Initial assessment to understand symptoms and overall health.
- Blood Tests: To check for liver function and specific markers like alpha-fetoprotein (AFP).
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, and angiography help visualize the liver and detect tumors.
- Liver Biopsy: A sample of liver tissue is taken to confirm the presence of cancer cells and determine the type.
- Laparoscopy: A surgical procedure using a camera to examine the liver and surrounding organs.
Stages
Liver cancer is staged based on how far it has spread:
- Stage I: Cancer is confined to the liver and has not spread to nearby blood vessels.
- Stage II: Cancer has spread to nearby blood vessels or multiple small tumors are present.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread to major blood vessels or nearby organs, excluding the gallbladder.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant parts of the body.
Treatment Options
Treatment for liver cancer depends on the type, size, and stage of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health:
- Surgery: Options include partial hepatectomy (removal of part of the liver) and liver transplant.
- Ablation: Techniques like radiofrequency ablation (RFA), cryoablation, and microwave ablation to destroy cancer cells.
- Embolization: Procedures like transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radioembolization to block blood flow to the tumor.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that specifically target cancer cells based on their genetic makeup.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells, often used for palliation.
Prognosis
The prognosis for liver cancer depends on factors such as the type of cancer, stage at diagnosis, liver function, and the patient’s overall health. Early detection and treatment significantly improve outcomes.
Living with Liver Cancer
Living with liver cancer involves regular follow-ups, managing symptoms, and support from healthcare professionals, family, and support groups. Advances in medical research continue to improve diagnostic and treatment methods, offering hope for better management and outcomes.
Liver cancer, though serious, can be effectively managed and treated with early detection and proper care. Understanding its types, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life for those affected.